What is On-Page SEO?

Attracting visitors to your website on a consistent basis plays an important role in the success of an inbound marketing strategy. Optimizing your pages and blog posts for search engines ensures that your content improves your businesses’ visibility to potential visitors by increasing your chances of ranking higher in search results.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is anything that you can do on a particular page of your website to improve its search performance and visibility. This can include work done on the content that your user sees as well as its source code. There are a number of factors to consider when optimizing your pages for search engines.
Factors of On-Page SEO
Content
The copy or content on your page or blog post is a primary factor in on-page SEO success. Generally speaking, your content should be relevant to the title of the page or blog and address it as completely as possible.
Good content from an SEO perspective is keyword-targeted. If you’re attempting to rank for a particular topic, include relevant keywords organically and naturally in your copy. Writing with your reader in mind versus a search engine is an excellent way to accomplish this.
Whereas you may feel compelled to include your keyword as frequently as possible (otherwise known as keyword stuffing), writing to explain a topic or have the reader understand why they’re on that page will enable you to naturally incorporate your chosen keywords.
Finally, your content must be unique. If you simply copy and paste content you found elsewhere, search engines will be able to identify it as duplicate content and prevent you from ranking higher than the original publisher.
Title
As I said previously, your content should be relevant to and address your page or blog’s title. Similarly, your title tag should be relevant to the content that follows it.
Your page’s title tag should be a concise and accurate representation of the content that a reader should expect to find when clicking on it. The title tag is essentially the first impression your website will give to a user on a search engine — make sure it’s a good one.
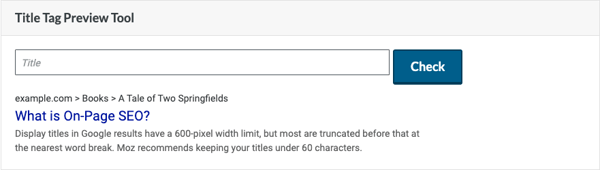
Ideally, your title tag also includes your targeted keyword. While limiting to 60 characters is best practice, some characters are larger than others, so there is some degree of flexibility. To avoid being cut off in search results, use a title tag preview tool to test whether your chosen title will appear effectively.
URL
Following your content and title tag, your page’s URL is the next prevailing factor. Much like a title, your page URLs should be concise, descriptive and include your targeted keyword. A search engine or a user should be able to discern the topic of your page by looking at the URL.
From a usability standpoint, your URL shouldn’t contain numbers. A listicle page with the number of items in its URL either cannot be updated or will eventually lead to inaccuracy if you chose to add or remove items from that list.
Additionally, if you want to align your URL strategy with a pillar page strategy, then the URL of your root page should be your targeted keyword, with other page URLs building off from there. For example, a pillar page strategy about demand generation would have the root page URL be the keyword “demand-generation” and a page within that strategy might be “demand-generation-tactics.”
Image alt text
Finally, the content on your pages isn’t just copy; it’s also photos and other digital assets. Effectively using image alt tags is the last area of focus when working with on-page SEO. Since search engines will crawl the source code of your pages, how you label your images and other assets will be considered as well.
Your alt text should include relevant keywords and be descriptive of the image in question both for search engine crawling and accessibility purposes. Alt text is not a place to stuff keywords, but rather a place to provide a written description of what’s in the image and feature your keyword if possible.
Some content management systems like HubSpot’s will pull alt text from an image’s file name. By following a clear process for naming your files, you can quickly address image alt text on your pages that is optimized for search engines and accessibility standards.
Other Factors of On-Page SEO
Meta descriptions
While not a factor for on-page SEO, meta descriptions can play a large role in whether or not someone decides to click on your link in a search result. Much like a title tag, your page’s meta description is a source of first impressions for your users.
By writing compelling and engaging copy in your meta description, you can drive clicks on your results. Search engines will often display relevant search terms in bold if they appear in a page’s meta description, so including keywords is best practice.
H1 tags
Unlike a title tag, your H1 tags do not have a direct impact on your on-page SEO. However, user experience and overall site quality does play a role in your ability to rank in search results. With that in mind, it’s best to align your title tags with your site design and heading styles for ensuring a consistent user experience.
On-Page SEO Tools
Since there are a number of factors that go into determining your page’s ability to rank in search results, there are tools you can use to ensure you’re checking all the boxes. 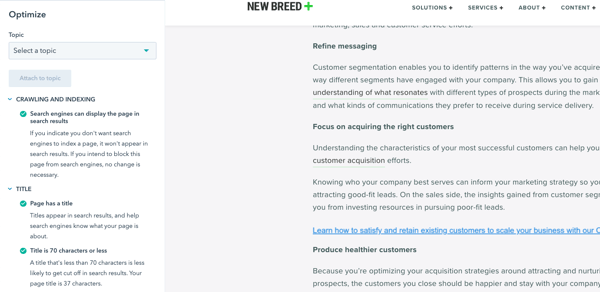
CMS tools like HubSpot’s feature a built-in optimize tool when drafting blog posts and website pages that check your titles, content, alt tags and more while offering tips for better performance. WordPress has a similar third-party tool, Yost.
Takeaway
Ensuring consistent high rankings starts with addressing your page’s content, title tag, URL and image alt text. While these four factors are weighted differently, they each play an important role in determining how your page ranks in search results.
Chris Singlemann
Chris is a Brand Marketer at New Breed where he is responsible for crafting design and video assets that support our brand. When he's not behind the camera, he enjoys kayaking and tending to his sourdough starter.





