Surprised to see your website on the lower end of the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages)?
That’s because some factors are pulling your SEO rankings down. And sadly, they might be doing damage without you knowing it.
So let’s get to the bottom of those factors in this post.
1. User Experience
Did you know that 79% of people leave a website if they don’t like it?
So if you’re focus is 100% on user experience, you’re making your visitors happy. And when your visitors are happy, you can also say the same for search engines.
Let’s break down this category:
Dwell time
Dwell time refers to the amount of time a visitor dwells on your website. If your website’s content is useful, this time should be longer.
For example:
- A dwell time of 2 seconds may indicate your visitor didn’t find your content useful, so they returned to the SERPs to look for a better website.
- A dwell time of 15 minutes could mean your visitor found your content useful, so they stayed and spent time on your website.
CTR (Click-Through Rate)
Click-through rate refers to how many clicks you get from the SERPs. A high CTR tells you that your keywords are performing well.
To measure CTR, you need to divide the number of clicks by the number of impressions:
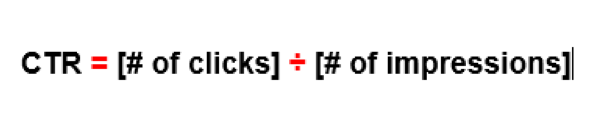 Bounce rate
Bounce rate
Bounce rate refers to how many visitors leave your website after checking out one page.
To calculate your website’s bounce rate, you need to find out how many people “bounced” and how many people entered that page. Then, divide the bounces by the entrances.
 Search intent
Search intent
Search intent refers to the search terms that your target audience is using.
After all, not all searches are one and the same. Finding out what searchers want gives you a clue on how to optimize your website.
There are four categories of searches:
- Navigational: searches that feature specific products, services and/or brand names. For example, “Jansport backpack.”
- Informational: most common searches that are meant to inform. For example, “How to make a pillow fort.”
- Transactional: searches for price or sales. For example, “HP laptop prices.”
- Commercial: searches with a mix of transactional and informational intent. For example, “where to buy a cheap phone.”
Page Speed
Page speed measures the page loading speed of your content.
Slow pages negatively impact your website. So, if your pages are taking too long to load, you should take steps to improve it.
First, analyze your website using Page Speed Insights. Once you get your score, you can work on how to increase your page’s speed. Potential fixes could include minifying JavaScript, CSS and HTML and enabling image and video compression.
2. Brand Queries
Not building your brand queries?
That’s a bad call.
After all, “brands are the solution,” according to Google’s Eric Schmidt. They’re what separates the bad companies from the good ones.
Bigger brand = higher rankings = stronger brand identity
With the help of your brand, you can also make ranking for your target keywords easier. If people are familiar with your brand, they’ll search for it along with a set keyword.
That said, it’s best to have a long-term keyword strategy in place. After all, long-tail keywords are much more effective.
For example, instead of just optimizing your website for the generic keyword “running shoes” you’d target “nike running shoes for women.” With this search, you’re ranking for “nike” (the brand) and “running shoes for women” (long-tail keyword).
3. Evolving Nature of SEO
Are you looking for a single factor that can magically lift up your rankings for years to come? Well, you need to know this: there isn’t one.
That’s because the future of SEO is not set in stone. The rules change all the time.
But of course, there are some fundamental principles that will stick around. When thinking of the future performance of your website, address:
- Crawlability: Allow the search engines to find your content
- Backlink profile: Build quality links because your content should be informative and highly authoritative. If you’re referencing or sharing content that isn’t yours, it should come from quality sources
- Site structure: Your website should be organized, and it should be easy to navigate
4. The Importance of Security
Security is paramount to your success because users want to feel safe when they’re online. I mean, who wants to visit a website that will put them at risk? That’s why Google prefers to send users to trustworthy sites.
Therefore to get into the good graces of search engines, you must switch to HTTPS. It is a ranking signal after all.
You can do this by getting a dedicated address from your internet provider. And then you should purchase an SSL certificate.
An SSL certificate authenticates your website. It also encrypts browsing history, personal information and other data. Ultimately, it builds credibility and also improves your rankings.
5. Poor presentation
How you present your website also affects your rankings. So this is where you let your creativity loose, but avoid going overboard. Your creative thinking shouldn’t cause a negative impact on your website. It should still be functional.
Bad spelling and grammar
Google’s Matt Cutts found a correlation between poor spelling and page ranking.
Especially with the Panda algorithm update in 2011, webmasters should mind their spelling. Their posts should contain facts and well-edited content.
To help you out with this, you can turn to editing software such as Grammarly and WhiteSmoke. These tools can be your writing assistant and correct the way you write as you go!
Duplicate content
Duplicate content is content that shows up in more than one place on the internet. For example, if you were to syndicate one of your blog posts on another website.
For website owners, this poses a problem. It’s rare for search engines to show many versions of the same content — they’ll choose just one version.
The result? Diluted visibility of duplicates.
And for a search engine, duplicate content poses a problem too. It brings about unnecessary confusion about:
- The version that should be indexed
- The version that should be ranked for query results
- How to direct link metrics (such as domain authority, trust and anchor text)
Keyword stuffing
Use keywords because they can help you amp up your organic traffic. And organic traffic is valuable.
So yes, you’re encouraged to use keywords. You should go with both short-tail keywords and long-tail keywords.
That doesn’t mean, though, that you need to stuff your articles with keywords. Otherwise, your content will appear forced and unnatural. And inarguably, that’s something that the search engines will frown upon.
Conclusion
If your site contains any of these negative SEO factors, you need to start fixing them immediately.
Remember, when it comes to your rankings, you could use all the advantage that you can get!
John Paulo Marquez
John is an animal-loving Digital Marketing Ninja and the Community Manager of MasterBlogging. He spends most of his waking hours testing cutting-edge digital marketing strategies and on his spare time, plays with his dog. Zeus. You can follow him @J_PMarquez.





